Spring boot 3 에서의 Spring Security 의 변화와 설정 방법 알아보기
아 이제는 security 에서도 빨간줄이 나타난다구요? 그럼 이쪽에서 광명 찾으세요.
1. Spring Boot 의 버전 변화
인텔리 제이에서 스프링 부트 프로젝트를 생성 하면
이렇게 3.2.0 버전으로 생성됩니다. 별생각없이 이전 프로젝트(3.0.x) 에서 시큐리티 설정 부분을 긁어왔는데…
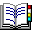
빨간줄에 마우스를 올려보니…
왜 이렇게 맨날 뭘 없애는거에요… 뭐가 바꼈는지 확인하기 위해 공식 문서를 들어가봤습니다.
2. Lambda DSL 사용

제일먼저 눈에 띄는 것은 람다식을 사용 하라 는 것 이였습니다. 공식 문서에서는 아래와 같은 이유를 들었습니다.
- 이전 방식에서는 반환 유형이 무엇인지 알지 못한 채 어떤 객체가 구성되고 있는지 명확하지 않았습니다. 중첩이 깊어질수록 혼란스러워 졌습니다. 숙련된 사용자라도 자신의 구성이 실제로는 다른 작업을 수행하고 있으면서도 특정 작업을 수행하고 있다고 생각할 것입니다.
- 일관성. 많은 코드 기반이 두 가지 스타일 사이를 전환하여 불일치를 발생시켜 구성을 이해하기 어렵게 만들고 종종 구성 오류를 초래했습니다.
2.1. 그래서 어떻게 바꾸라는 걸까? 🤷🏻♀️

공식문서에 나와있는 예시를 들어보겠습니다. 첫번째 방식은 일반적으로 사용하던 방식입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
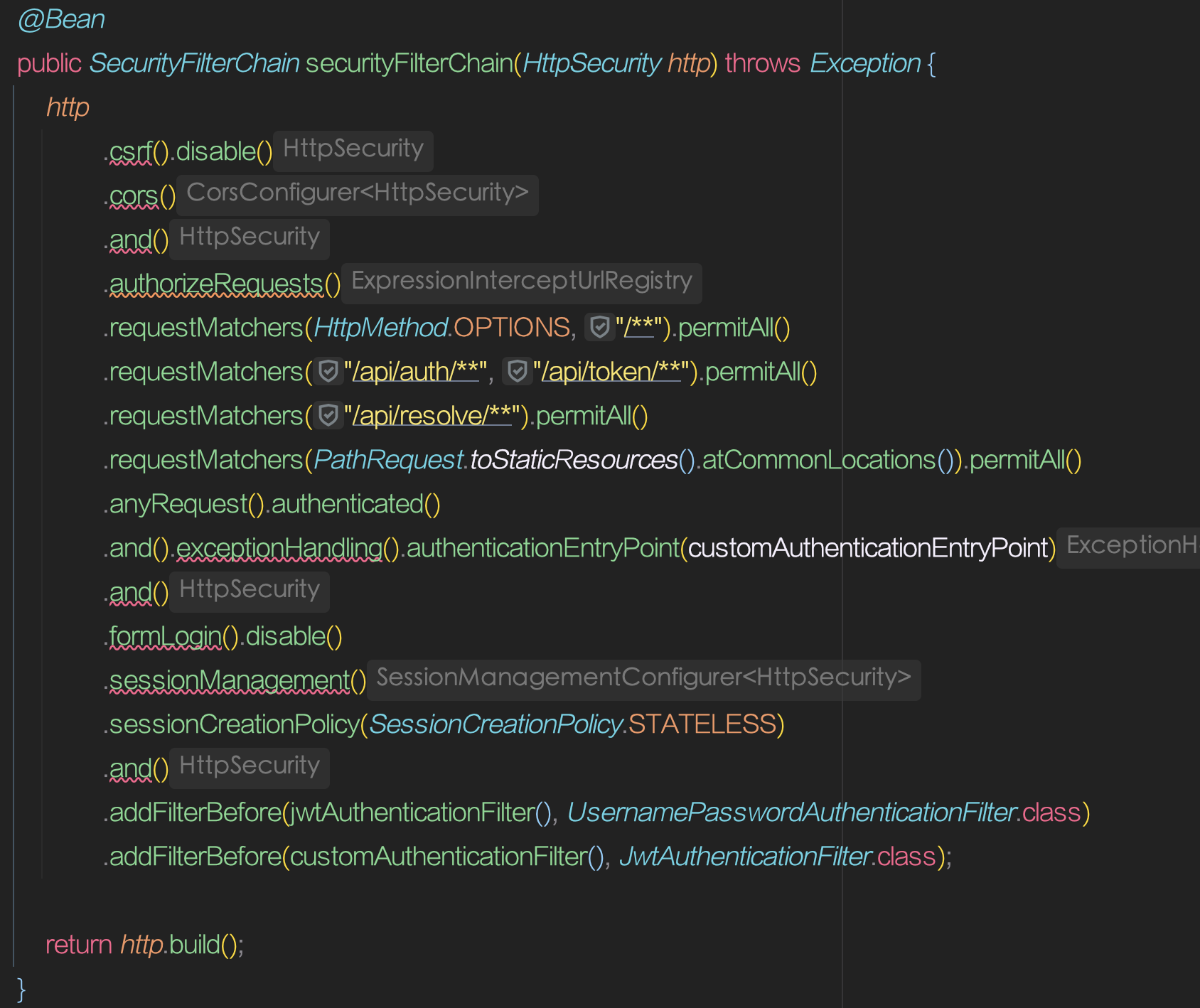
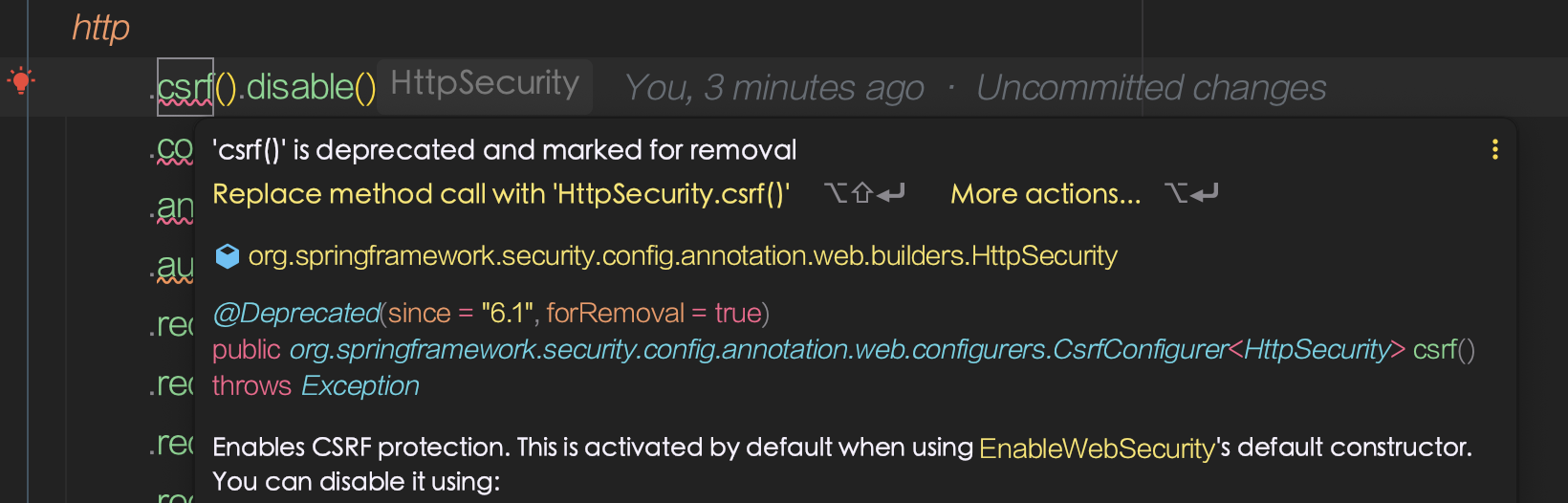
http
.authorizeHttpRequests()
.requestMatchers("/blog/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.rememberMe();
return http.build();
}
}
공식문서는 위의 코드를 람다식을 사용하여 함수형 으로 변경 하라고 하는데요, 이렇게 하면 아래의 장점을 가진다고 합니다.
- 자동 들여쓰기를 사용하면 구성을 더 쉽게 읽을 수 있습니다.
.and()를 사용하여 구성 옵션을 연결할 필요가 없습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@Configuration
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityWebFilterChain springSecurityFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) {
http
.authorizeExchange(exchanges -> exchanges
.pathMatchers("/blog/**").permitAll()
.anyExchange().authenticated()
)
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
.formLogin(formLogin -> formLogin
.loginPage("/login")
);
return http.build();
}
}
3. 적용해보기

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SecurityConfiguration {
...
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.cors(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.authorizeRequests((authorizeRequest) ->
authorizeRequest
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.OPTIONS, "/**").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/api/auth/**", "/api/token/**").permitAll()
.requestMatchers("/api/resolve/**").permitAll()
.requestMatchers(PathRequest.toStaticResources().atCommonLocations()).permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.exceptionHandling((exceptionHandling) ->
exceptionHandling
.authenticationEntryPoint(customAuthenticationEntryPoint)
)
.formLogin(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.sessionManagement((sessionManagement) ->
sessionManagement
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
)
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(customAuthenticationFilter(), JwtAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
...
}
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.